What Did Mesopotamians Do For Makeup
The cradle of civilization, Mesopotamia, was the birthplace of many valuable inventions and discoveries. It was hither that agriculture began. Irrigation and farming were commonplace in this area because of the fertile country between the Euphrates and Tigris rivers. The invention of agriculture made it possible for humans to stay in the same identify for a longer period of time without depending on hunting.
The earliest form of writing was invented in Mesopotamia as were the first ways of transportation: the chariot and the sailboat. Nigh innovative ideas that we take for granted today were invented or discovered in Mesopotamia. Here are the top 11 inventions and discoveries of ancient Mesopotamia:
11. The Wheel

The kickoff wheel wasn't used for transportation. The bicycle was commencement invented as a potter'due south cycle and was believed to accept existed effectually 3500 BC.
Even though the wheel is believed to accept first existed in ancient Mesopotamia, the oldest bike named the Ljubljana Marshes Wheel was discovered in Ljubljana, the capital of Slovenia, in 2002 and dates back v,150 years.
The wheel was used as a luxurious form of transportation for the wealthy, but was also used for irrigation, pottery making, and milling. The invention of the chariot and other of import innovations in history were based on the invention of the wheel.
10. The Chariot
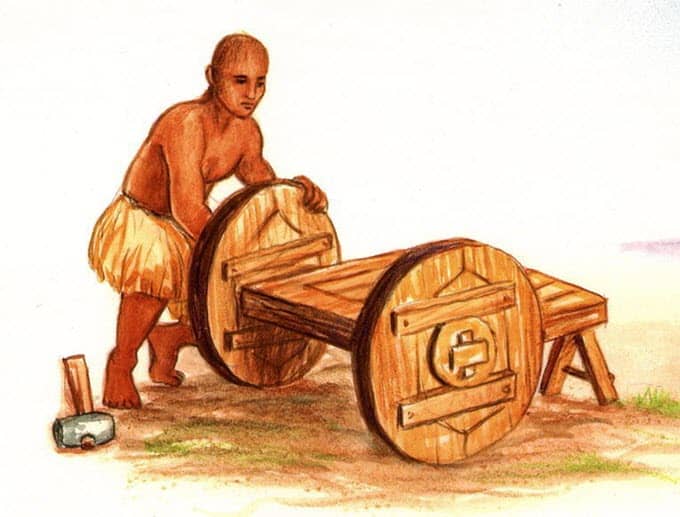

Over fourth dimension, humans learned to domesticate horses, bulls, and other useful animals and the invention of the chariot or carriage followed on from their domestication. The chariot was the first means of personal transportation, and has been used for years in warfare, sport, and for general use. The structure of the earliest chariots was from light woods with a bentwood rim. The first chariot appeared effectually 3200 BC in Mesopotamia and was adopted by most every civilization until motorized transportation came into existence. Chariots were mainly used for personal transportation by royalty and the wealthy.
9. The Sailboat
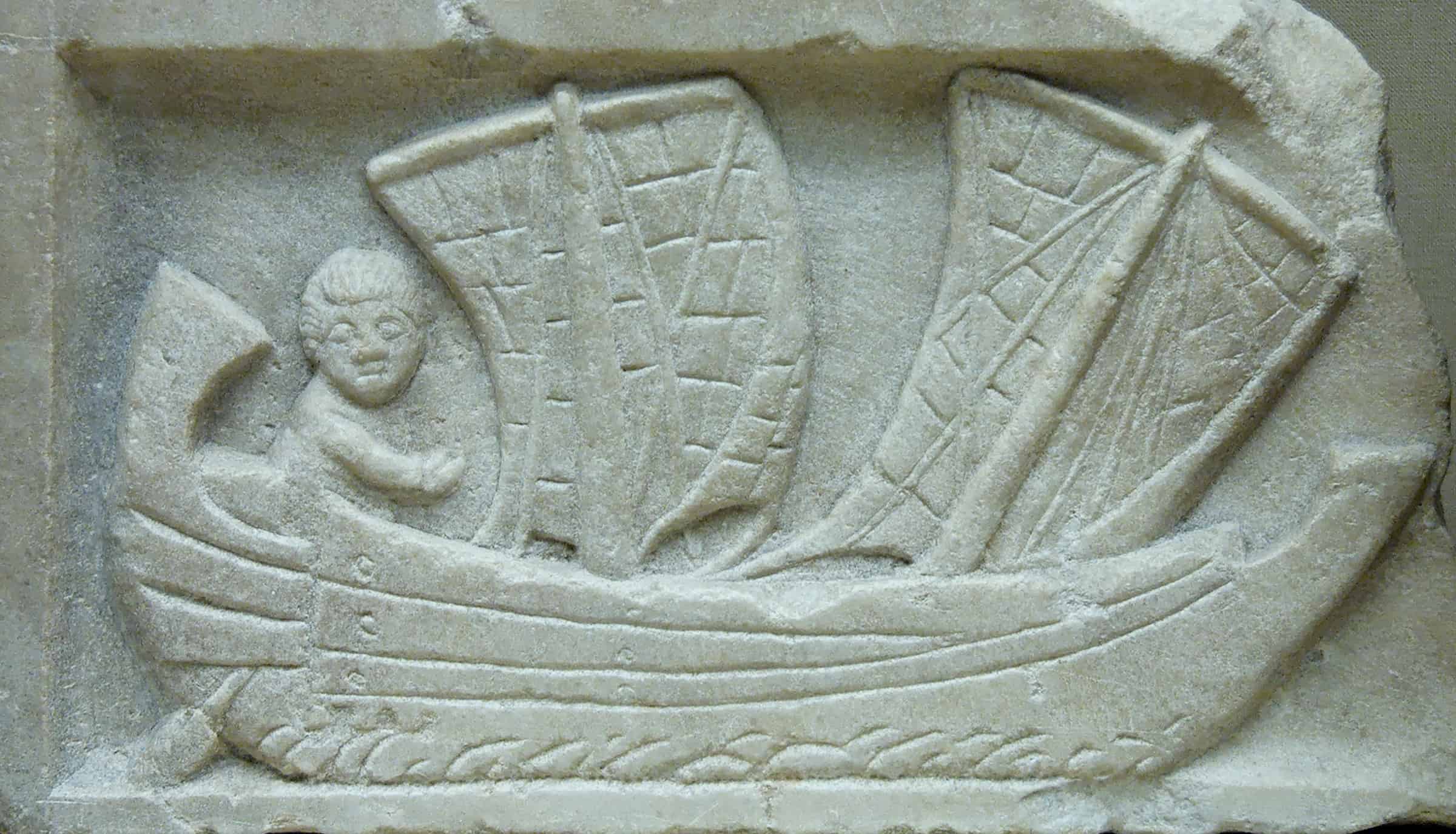

Transportation past land was difficult and took an enormous amount of time. The Sumerians realized that transportation via sea would be a lot easier and more than convenient. The first gunkhole was invented and used on rivers and needed to exist navigated by humans. The offset sailboat was a elementary, primitive blueprint and aided in trade and commerce. It was initially used to cross the Tigris and Euphrates rivers for fishing and to explore other areas.
The archaic sailboat was square in shape and the sail was made of fabric. The direction of the sailboat couldn't be changed. If the current of air didn't blow in the direction they wanted to go, they had to look for the current of air to change in their favor.
8. The Turn
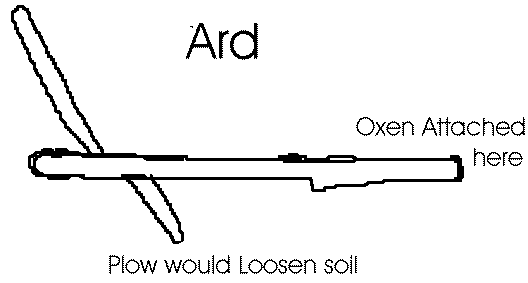
Humans learned to domesticate animals and utilise them to make daily life easier. In Mesopotamia, man first harnessed the ox and developed the kickoff turn called the "ard." The earliest plow was fabricated of wood and was very heavy. The major trouble with the plow was that the dirt would stick to it and needed to be removed manually. Information technology too did not work in thick grass. The invention of the turn in Mesopotamia helped the hunter-gatherer groups to stay in the same identify and use agriculture for food rather than hunting.
7. Time

The Mesopotamians developed the concept of fourth dimension, dividing time units into 60 parts, which eventually led to 60-second minutes and threescore-minute hours. The Babylonians made an astronomical adding in the base 60 organisation inherited from the Sumerians. The number 60 was called considering it was hands divisible by vi.
6. Astronomy and Star divination

The concept of star divination was developed during the Sumerian period when even everyday incidents had a spiritual meaning. Information technology was believed that every good or bad thing happened for a reason.
Ancient astrologers observed the location of the planets and advised people in high social or political positions according to these observations. Astronomical mythology, similar the concepts of the constellations such equally Capricorn, Leo, and Sagittarius, was handed down to the Greeks by the Sumerians and Babylonians and is withal in use today.
The constellations were also used in solar day-to-day activities. They were relied upon to mark the seasons for harvesting or sowing crops. They too mapped the motion of the heaven, the sun, the stars, and the moon, and were used to predict angelic events like eclipses.
5. The Map
The oldest map was discovered in Babylonia around 2300 BC. Aboriginal cartography used in Babylonia were simple sketches on clay tablets. One dirt map discovered in Mesopotamia illustrates the Akkadian region of Mesopotamia (present-mean solar day northern Iraq). It covers a small area and was generally used as a urban center map for armed forces campaigns, hunting, and trading.
Even though the map was first invented in Mesopotamia, Greek and Roman cartography became more advanced and the concept of a spherical world developed by the Greek philosophers in 350 BC immune geographers to develop the map further.
iv. Mathematics
When the civilization began to flourish, people started to trade and they needed an accurate system to count the appurtenances that they gave and received. The Sumerians were the first people on globe to develop the concept of counting.
They also developed the sexagesimal system, or base 60. The sexagesimal organisation helped to develop concepts like the 360-degree circle and the 12-month twelvemonth.
They used 12 duke to count on one hand and some other five fingers on the other hand. The Babylonians used base 6 (our modern organization uses base 10), where digits in the left cavalcade represent large values.
The concept of goose egg was developed past the Babylonians. People understood the value of having aught, but the concept of numerical zero wasn't invented before then. Many scholars believed that the concept of zip was developed by the Babylonians and followed and adjusted past various civilizations throughout the world. Some also contend it was originally invented in India.
3. Urban Civilization
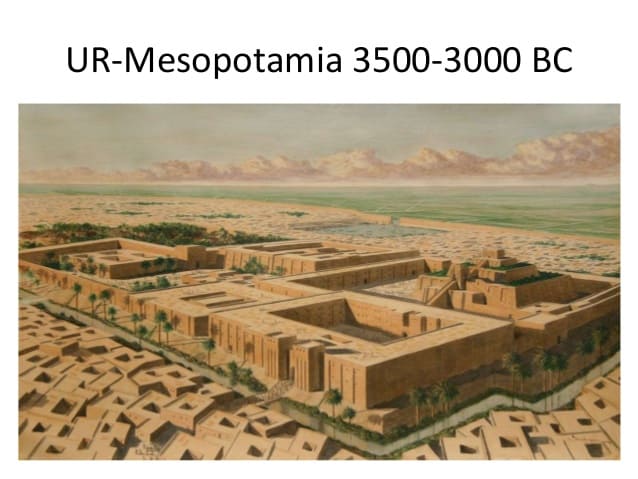

Oft known as the cradle of civilisation, Mesopotamian developed the concept of urbanization. For the first time in a history, humans started to settle in a specific place. The invention of agronomics fabricated it possible to feed more people and animals living in a single location. People learned to trade, and the concept of taxes was developed.
Mesopotamia emerged as one of the first cities of the world to be built with sun-dried bricks. The urbanization in Mesopotamia started in the Uruk period (4300–3100 BC) and the largest settlement in the history of mankind ever to be built was done then using monumental mud-brick buildings effectually 3200 BC. The city was surrounded by huge walls built by King Gilgamesh.
ii. The First Class of Writing: Cuneiform
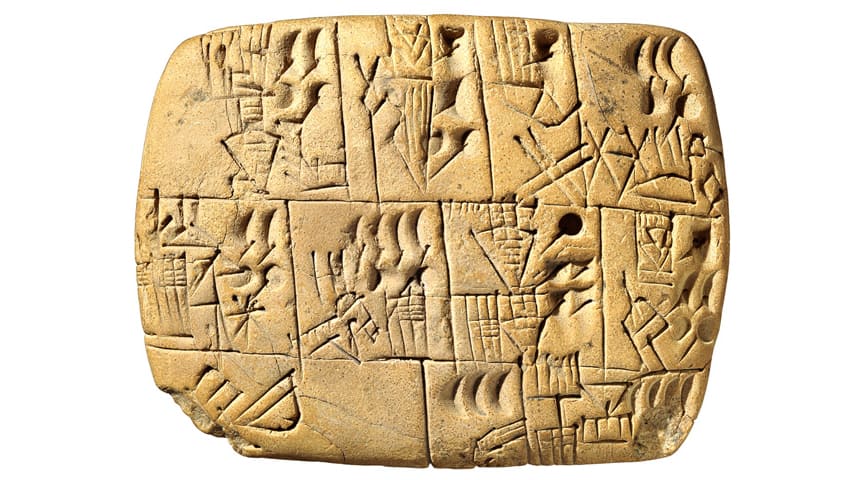

The Sumerians adult the first form of writing called "cuneiform" to maintain business organization records. Information technology was mostly used in trade, where merchants recorded information such as the amount of grain traded. The Mesopotamians also used writing to record daily events similar astronomy.
Cuneiform evolved as a simple pictograph. For example, the pictograph for a horse might be a small image of a horse. The writer had to drag the tip of a stylus beyond wet dirt to create a shape. Information technology was hard to call back every grapheme and it would have 12 years for a person to larn to write in cuneiform.
The symbols were reduced to 600 words by 2900 BC and scribes (people who were hired to write) eventually changed the writing from a drawn epitome to a stamp or imprint using a reed stylus with a wedge-shaped tip. Cuneiform script was used by the Assyrians, Elamites, Hittites, Babylonians, and Akkadians for about iii,000 years.
i. Agronomics and Irrigation
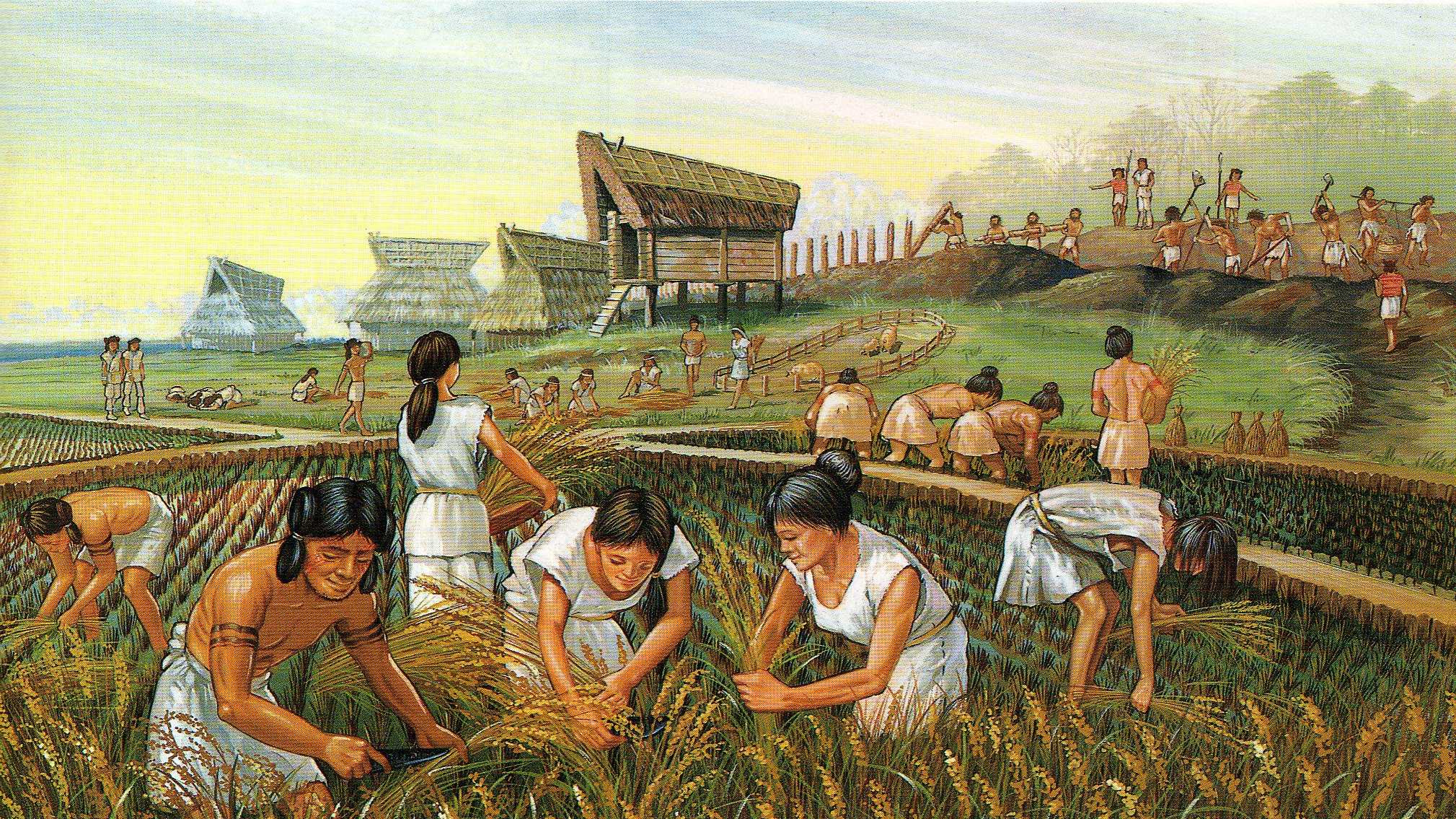

Ancient Mesopotamian farmers cultivated wheat, barley, cucumbers, and other different foods and vegetables. They used stone hoes to plow the ground before the invention of the turn.
The Tigris and the Euphrates rivers that surrounded Mesopotamia made irrigation and farming a lot easier and more convenient. The Mesopotamians learned to control the menstruum of water from the river and used it to gargle crops. During the main growing season, the flow of water was properly regulated. Each farmer was allowed a sure amount of water which was diverted from a canal into an irrigation ditch.
Conclusion
About of the inventions and discoveries of the aboriginal Mesopotamians became more advanced in after civilizations. Yet, Mesopotamian inventions led to very bones things that were needed for humans to settle in a grouping such as writing, agriculture, and urban civilization.
Acquire the inventions of other civilizations:
- Top ten Ancient Roman Inventions
- Top ten Inventions and Discoveries of Ancient Greece
- Top 18 Ancient Chinese Inventions and Discoveries
- Top 10 Inventions of the Mayan Civilization
- Top x Inventions and Discoveries of Ancient Egypt
Source: https://www.ancienthistorylists.com/mesopotamia-history/top-11-inventions-and-discoveries-of-mesopotamia/
Posted by: berryhalseara.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Did Mesopotamians Do For Makeup"
Post a Comment